Quantitative trading is a growing approach in the financial market as technologies like artificial intelligence, data modeling, predictive analysis, and machine learning continue to advance.
As a result, the number of quantitative traders and hedge funds is continuing to grow internationally. Today, some of the top-performing funds in the world are those that use quantitative approaches and strategies. They include funds like Two Sigma, AQR, and Renaissance Technologies.
Quantitative trading has numerous advantages. For example, it does not have a bias on direction of assets or the performance of indices like the S&P 500 and Nasdaq 100. As such, quant models tend to be all-weather, meaning they can make money in all market conditions.
This article will get deeper into the concept of quant trading. We will look at how it works and some of the top things you need to know.
Table of Contents
What is Quantitative Trading?
Quantitative trading is a day trading approach that involves using mathematical models to find trading opportunities. The idea is that several models, when carefully done, can help you predict the future. All day traders can use this approach today.
Those traders who are also excellent in mathematical modeling and coding can build their codes from scratch. At the same time, those who don’t have this knowledge can easily buy already-built robots in online marketplaces. One of the best-known marketplaces is the one run by MQL, which owns the popular MetaTrader 4 and 5.
Quant vs algorithmic
Quantitative and algorithmic (algo) trading are often used interchangeably but there are minor differences between the two. The core of quant trading is the use of mathematical models to predict the short-term or long-term movement of an asset.
These models are based on various mathematical areas like predictive analysis, calculus, and machine learning. Some traders also use external data models like weather, location data, and satellites to predict asset movements.
For example, a quantitative trader can look at weather patterns to predict the demand and supply of agricultural commodities.
Algorithmic trading, on the other hand, refers to the use of simple or advanced models to analyze the market and execute trades. These algorithms can be as simple as using moving averages to predict the next price action. They can also be highly complicated where they use tens of data points.
In all, quant and algo trading have some differences in theory. However, in reality, they are often used by the same people and in some ways.
How quant trading works
A common question you may have is how quant trading works. While the implementation of quant trading is a bit complex, its fundamentals are relatively simple to understand.
Quant trading works by automating manual trading concepts. For example, assume that you are a day trader who focuses on three technical indicators: moving average, the Average Directional Index (ADX), and the Relative Strength Index (RSI).
In this case, you plan to initiate a buy trade when these conditions are met: 25-period and 50-period moving averages crossover, ADX rises above 25, and the RSI moves above 50. In this case, you can wait for these conditions to happen and then you can implement a trade.
Alternatively, you can create software that opens a trade when these conditions are met. You can also ‘tell’ the software to continually assess tens or hundreds of assets at once. In this case, the quant tool will do exactly that and open positions for you.
Most importantly, the quant tool can have risk-management parameters such as position sizing, stop-loss, and take-profits. Also, in addition to technical analysis, the tool can follow fundamental data like earnings and economic data.
The core of quantitative trading is that it relies on mathematical models to predict where an asset will move.
What is market microstructure?
The concept of market microstructure has been around since 1976 when it was developed by Mark Garman of UC Berkeley. It is a study that aims to understand the general structure of the financial market and how it works. It focuses on the theoretical, empirical, and experimental research on the market.
When used well, the concept of microstructure can help a trader or a portfolio manager understand how the market is moving. Most quant traders use this approach to understand some key issues like market structure and design, price formation and discovery, volatility and liquidity.
While these issues don’t necessarily move an asset, having a good understanding of them can help you know the state of the market. For example, liquidity and volatility can help you know more about transaction costs.
Related » Prop Trading vs Quant trading
Degree or qualifications needed in quant trading
Quant trading is different from other types of manual trading approaches like trend-following and scalping. Because it relies on in-depth models, it is important for you to have knowledge and expertise in key academic areas.
These areas are also useful if your goal is to get a job in quant trading firms like Renaissance Technologies, D.E Shaw, AQR Capital, and Two Sigma. These firms will mostly hire people with deep academic qualifications in several quant areas.
Therefore, the most important degrees you need to have are in:
- Mathematics
- Computer science
- Software engineering
Some of the top fields you need to be good at include Python, applied mathematics fields like fluid mechanics and cryptography, linear and non-linear time series, and machine learning techniques like Deep Neural Network (DNN) and Long Short-Term Memory. Also, you should know areas like multivariate methods like factor analysis.
These fields are taught in many universities. Alternatively, you can use several online companies like Coursera and Udemy to learn more about them.
Additional skills in quant trading
In addition to the hard skills, there are other soft skills that you need to become successful in quant trading (in addition to the standard ones for a day trader). Some of these skills are:
- Teamwork – If you are working as part of a team, you must have quality teamwork and interpersonal skills. This will help you have a conducive working environment.
- Work under pressure – Developing quant models is not easy, even for the most experienced traders. It also takes a lot of time. Therefore, you must be comfortable working under intense pressure.
- Risk management – You must always have the best risk management strategies when trading. This approach will help you reduce your market risks while ensuring that you are making money.
Quantitative trading systems
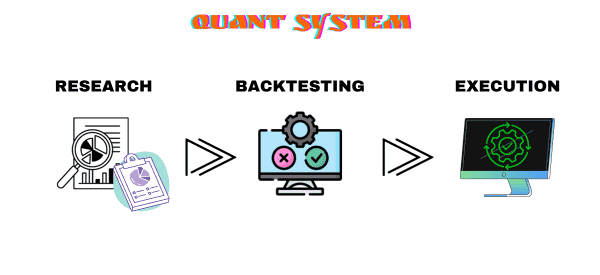
There are three essential parts in quantitative trading systems. First, there is the research part, which involves doing studies about financial assets and various financial models. This research is often based on a person’s experience in the quant trading industry.
The other part is known as backtesting. This is a process where you take your quant model through a testing process using historical data. When done well, backtesting can show you whether the quant model will work out well in the financial market.
Backtesting should always be accompanied by forward testing, which is the process of using current data to predict the next price action of an asset. In most cases, this usually happens using a demo account like our TMS™, which provides real market data.
The third part of a quant trading system is execution. It is a process where you move the system from a demo into a real account. The goal is to execute the model and monitor it to see its success.
Why quantitative trading is the future of trading and why you should learn it
#1 – Barriers Removed
In the past, to create your own robot, you needs to have a background in computer science or in software development.
This is because one needed to take time and develop the code which will execute trades. This prevented most people from developing these applications because not many financial professionals have experience in coding.
Today, most online brokers have developed platforms to help people with no coding experience to develop their robots. They have drag and drop tools and instructions which enables them to create robots within minutes.
#2 – Knowledgebase Available
In the past, to learn about quantitative trading, one needed to go to school and learn about coding. This was a major barrier to entry because many people saw no need for this training. Today, traders have access to information on how to create trading bots.
This information is available in various quant trading tutorials and videos which guide people on how to develop these codes. There are also many online videos that guide people to develop the robots. Or, you can simply ask artificial intelligence for help (but don’t trust it blindly!).
#3 – The Big Thing Now
As mentioned in the introduction, most hedge funds are now turning to automated trading. Most hedge funds are now experiencing a period of low growth and increased outflows.
On the other hand, automated hedge funds such as Betterment are experiencing a period of growth. Therefore, as the trend and the returns continue to grow, chances are that most people will focus on this new trend.
#4 – A Simple Process
Before you start practicing algorithmic trading, chances are that you feel that it is a difficult process. However, as you become more acquainted with the system, you will realize that it’s a simple process. Once you have mastered the art and science of combining various indicators you will have a better time trading.
Remember that the key to successful algo trading is to create a good system and backtest it for a period of time. If you prove without any reasonable doubt that your system is good, then you will have an easy process of trading.
#5 – It Works
The last reason why algorithmic trading is the future is that it is an accurate method. The best way to look at this is to compare hedge funds that use the systems and compare it with those that don’t.
In the 2008 financial crisis, while most hedge funds closed shop, James Simmon’s firm reported its best year so far with an 80% return.
The fund has also never had any negative years. This means that when well-executed, algorithmic trading works. The key is to develop a good system and then backtest for a good period of time.
How to quantitative trade
There are several approaches to quantitative trading. But at the core, QT is just an automated method of manual trading. For example, if you use double moving averages to identify buying and selling opportunities, you can create a robot that will implement that when you are not around.
First of all, you need to have a trading strategy in mind. For example, if you are a scalper, you can find a quantitative robot that focuses on the scalping strategy. Let’s see together some of the most popular strategies to use.
Arbitrage
This is a trading approach that aims to take advantage of pricing differences between financial assets. It is often known as pairs trading. For example, you can use this approach to trade two ETFs that have similar components, meaning that they move in the same direction.
You can buy the SPY ETF and then short the VOO ETF, which tracks the S&P 500. In this case, one of the funds will rise while the other one will retreat. Therefore, your profit in this case will be the difference between the two.
There are other types of arbitrage in trading, including pure arbitrage, risk arbitrage, merger, triangular, convertible, and statistical arbitrage. Convertible arbitrage involves buying a convertible bond and shorting the underlying stock.
Merger arbitrage involves buying the stock of a company being acquired and shorting the acquirer. It is also a bet on whether the deal will be allowed to be completed by regulators.
Mean reversion
This is a trading strategy that involves going against the trend. The idea is that some financial assets are either highly expensive or extremely cheap and that their prices will ultimately reverse.
For example, if a stock surges from $10 to $14 within a few days, you can assume that further gains will be limited and then short it. Similarly, if the stock moves from $15 and drops to $12, you can assume that it will bounce back.
These quant models aim to look at extreme price movements in the market and then go in the opposite direction while using proper risk management strategies.
Directional strategy
Also known as trend-following, this is a trading approach that aims to take advantage of the underlying trend in the market. The goal is to buy an asset that is already rising and a short one that is already falling.
In most cases, the idea is that an asset will continue moving in a specific trend until something dramatic happens.
Why data matters
In quant trading, data is one of the most important parameters that must be gotten right. In fact, it has been argued that data is the backbone of any quantitative trading system. It’s the engine that powers any system.
If a single digit or decimal point is left out when developing the system, chances of losing your trades are very high.
Price data and fundamental data
There are two main types of data when developing algorithms. These are: price data and fundamental data.
Price data includes a number of parameters such as the price of the asset, trading volumes of assets, size of the trade, and the information derived from transactions among others. In simple terms, price data refers to the entire order book which shows a continuous series of all bids and offers of an asset.
On the other hand, fundamental data are more complicated and refer to a number of data types that are difficult to categorize. They refer to any other data that is entered that is not related to the price of asset. Some of the good types of fundamental data are: price to book ratio, financial performance, and sentiment among others.
Macroeconomic data such as inflation and interest rates can also be said to be fundamental data.
Understand the data
To know how to use the data, one needs to understand where to get the data from. In quant trading and high frequency trading, the accuracy of the data must be accompanied by the timely delivery of the data. A microsecond in the financial market can mean huge losses.
There are many sources of data which include: regulators (filings relating to large owners), government agencies (mostly for fundamental data), news agencies (such as Bloomberg), proprietary data vendors (such as Markit), and corporations.
Common issues
After getting the data, a common problem faced by many quantitative traders is on cleaning the data. This is a common problem that has led to the downfall of many quant traders. A common problem with quants is missing data especially where the data is not supplied at the given time by the data supplier.
This can be solved by building a system that understands when the data is missing. This system will not take irrational decisions that can lead to significant losses.
Another problem is what we call look-ahead bias. This is when you assume that you could have known something before it was possible to know it. As stated before, data is the machine that moves quant systems.
Hedge funds such as Renaissance technologies and Citadel have for years made more than 20% returns using quantitative systems. The LTCM mentioned above is a good example of what not to do when using quant systems. The fund almost lost 100% of its capital as a result of poor data sets combinations.
Therefore, you should carefully take your time when developing your system. You should back test and forward test the system to ensure that everything is right.
Pros and cons of quant trading
Pros
- It is an approach that works well, especially for experienced traders.
- It can be highly profitable since the quant models can analyze various markets at the same time.
- Emotion-free – Unlike other approaches, it allows for emotion-free trading since trades are executed by the robots.
- Less human errors – The approach has less human errors since it mostly works using algorithms.
- Faster transactions – Trades are executed at a significantly faster pace compared to other approaches.
Cons
- Quant models can fail – These models don’t always work, which explains why there are significant risks involved.
- It takes time to learn – It takes more time to learn and implement quant trading approaches in trading.
- It takes more skills – Quant models are usually more skill-intensive.
FAQs
How can I build my own quant trading model?
The process of building your own quant model is often long and complicated. You will first need to have the practical hard skills mentioned above.
After this, you should build these models, backtest them, forward test, and then implement them in the financial market.
How long does it take to build a quant model?
In most cases, these quant models usually take a few months or years to build. But the process will depend on your experience in the industry. Highly experienced traders can come up with these models within a few days.
Can quant trading work in day trading?
Yes it can. Most people who employ the quant trading approach are often day traders.
Final thoughts
Quantitative trading is a relatively new approaches to the financial market. Indeed, the volume of trades executed algorithmically has increased substantially over the years. In fact, trillions of dollars-worth of trades are executed algorithmically every day.
Fortunately, anyone can use the strategy either by building his own algorithm or by buying an already-made product.
External Useful Resources
- Discover more about Quantitative trading on Investopedia
- Read more on Quantitative trading on Quantstart