The stock market is among the most active in the developed world. In the United States, the volume of stocks traded every day is worth trillions of dollars.
However, the biggest challenge for stocks is that trading hours are usually limited.
For example, in the United States, the New York Stock Exchange (NYSE) and Nasdaq are open from 9:30 am to 4:00 pm. The same is true for other exchanges around the world.
To solve the problem, the main exchanges in the US have started extended hours trading. These hours are also known as premarket and after-hours trading.
Table of Contents
What is Premarket Trading?
If you watch financial media frequently, you will realize the commentators talk about how stocks are trading even before the exchanges open. You also here them talk about how the indices are trading before the market opens. When you hear them talking about these, they are basically talking about premarket trading.
Similarly, stocks continue to trade for a few hours after the exchanges are closed. This is known as afterhours trading.
Related » How a trader’s workday is scheduled
Premarket trading hours
American bourses started to embrace the concept of extended hours in the 1990s. That is because these exchanges were facing increasing competition from foreign bourses, especially those in Hong Kong and London. Most of these exchanges tend to have longer trading hours.
Therefore, the NYSE and Nasdaq decided to allow premarket trading, which starts at 4:30am to 9:30, when the market opens. At the same time, they decided to offer afterhours trading after the markets close. Still, many brokers have their execution details for afterhours trading.
How Premarket session works
The premarket session is different than the regular session. For one, the session does not include all assets. As such, there are stocks that you cannot trade during the premarket session. Also, the regular session has some more tools. For example, when trading in the regular session, you have access to market makers if your broker allows you to access them.
In addition, the premarket session does not offer direct execution. In other words, you can only execute orders using pending orders.
The premarket works like this. Brokers like Robinhood and Schwab partner with companies that match customer orders in an electronic method. When the market opens, the companies switch to the main market makers.
How does Premarket trading Works? Differences with standard trading
Premarket trading is different from the standard trading in several ways. Let’s go over the key divergent points.
Orders & Limit Orders
First, in standard trading, orders are placed instantly at the market prices. This is not the case with premarket and afterhours trading. In the two, only limit orders are placed. A limit order is an on order in which you direct the broker to open a trade in future.
For example, a broker like Schwab processes premarket orders between 07:00 am and 9:25 eastern time. A broker like Interactive Brokers allows premarket trading by IBKR Pro from 04:00 EST until the market opens. For IBKR lite customers, the trading starts at 07:00 am.
Number of Shares
Another difference between the two is on the number of shares you can buy during the period. In the standard market, you can buy any number of shares you want. However, in the premarket trading, some brokers have other requirements.
For example, Schwab only allows a maximum of 25k shares to be traded during the extended hours.
Volume
In addition, volume is an important aspect for any trader. An important characteristic of afterhours trading is that the volume is usually limited because the number of participants is usually a bit small.
Therefore, as a trader, you should be concerned because of the limited volume.
Key Premarket Movers
There are several reasons why shares of a company moves sharply during the premarket hours.
Earnings
First, the stock can be relatively volatile if the firm releases its earnings. For example, if the company reports better-than-expected results, the share price can move relatively higher and vice versa.
Major News
Second, the shares can be volatile if the company reports a major news. For example, in 2020, Moderna share price rose sharply after the company announced that it was testing a covid-19 treatment.
Macro Events
Third, stocks can move because of macro events. For example, recently, shares of energy companies declined in premarket trading after the price of crude oil went negative.
How to find premarket movers
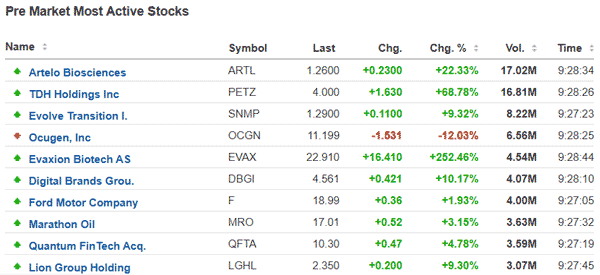
As a trader, one of the best things that can simplify your trading is being able to find premarket movers in the market. Fortunately, there are several methods of doing this. First, you can use a free watchlist service that sends you the most active stocks and the reason for their movements.
Second, you can use free platforms like Investing.com and Market Chamelion to find companies that are showing a strong performance in the market. You can then dig deeper into these companies. The chart below shows some of these market movers.
Finally, you can use popular media platforms like CNBC and Bloomberg to check out companies that are showing significant movements.
What is a premarket gapper?
Unlike forex and cryptocurrencies, stocks are usually traded in a limited period in a day. As such, there tends to be a gap between when the market closes and when it opens.
For example, if a stock closed at $25 and then opened at $30 the followingday, the gap between is known as a gap. It is one of the riskiest thing in the market when you are long or short a stock.
The chart below shows a gap on the Zillow stock.

Premarket vs extended hours
The premarket session is often confused with extended hours but the two are different. While the premarket session happens in the morning, extended hours usually come after the market closes.
When the regular session ends at around 4pm, exchanges continue providing trading solutions to their customers. In this period, traders can analyze stocks and then implement them. However, like in the premarket session, the trades are usually implemented using pending orders.
In most cases, trading in premarket hours is usually better than in extended hours. This is simply because the premarket session is followed by the regular session. As such, there is usually minimal risk of a major gap happening between the premarket and normal session.
Risks of trading in premarket session
While trading is generally risky, there are risks that emerge when you trade in premarket trading. These include:
- First, although it is not common, there is a risk that the stock will form a gap at the intersection of the premarket and regular session.
- Second, there is a risk of low liquidity in the market since many institutional traders start working during the regular session. This low liquidity can lead to a higher spread when the market opens.
- Third, the session is often highly volatile. While volatility is good for experienced traders, it can have major challenges for inexperienced ones.
- Finally, if you have a direct market access broker, you will not have access to the market makers during this time.
Final thoughts
The premarket session is an important period for you to look at. In most times, you should take advantage of these moves to open trades and benefit from movements.
Still, you need to understand the risks involved because of low volume and that several brokers charge more for premarket trades.
External Useful Resources
- Pre-Market and After-Hours Trading Activities – Investopedia