The financial market is a dynamic ecosystem that processes trillions of trades on a daily basis. It works by matching buyers and sellers in the marketplace.
Brokers use different approaches. For example, most brokers in the US use the Payment for Order Flow (PFOF) model where orders are filled by a small group of market-makers.
Electronic Communication Networks are among these tools. In this article, we will explain what ECN is, pros, cons and how it works.
Table of Contents
What is an ECN?
Instinet, the first electronic communications network (ECN), was launched in 1969, giving a major boost to electronic trading. This was then revolutionized in 1971, when NASDAQ, the world’s first electronic stock market, was launched.
In the 1990s, ECNs such as Instinet and others rose to prominence by helping to make trading affordable for more people, offering greater liquidity, lower trading costs and transparency, transforming financial markets.
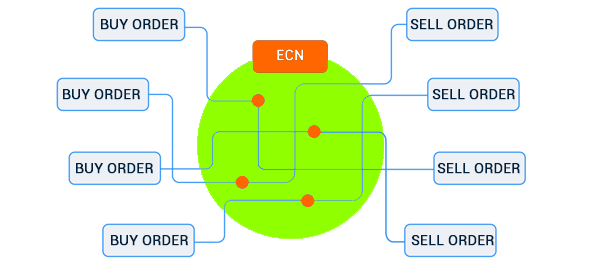
As the name suggests, the Electronic Communication Network is a network that matches buyers and sellers for securities in a market. It is a complex network that handles trades worth hundreds of billions of dollars every day.
The system consolidates the market activity from hundreds of other companies. As a result, it is able to offer tighter spreads, which leads to lower fees.
In summary, an ECN is a complex network that connects most brokers in the industry. It acts as a market-maker that matches these orders. By so-doing, the system can handle more trades per day and at a lower cost to trades.
ECN is different than the model that American companies like Robinhood and Schwab use to execute their orders. These companies use the PFOF model that involves market-makers like Virtu Finance and Citadel Securities.
American brokers also shift to ECN in their daily operations. Since the stock market closes in the afternoon, the companies shift to electronic networks during extended hours and pre-market sessions. Only limit orders are allowed in these periods.
What are ECN brokers?
An ECN broker is a company that provides its services using the model described above. These companies don’t rely on market-makers. Instead, they depend on a whole system of communication technology that links multiple financial brokerages.
And unlike in PFOF, the ECN technology cannot trade against a trader.
A common criticism of Payment for Order Flow is that it lets high-frequency traders open trades in the opposite direction of the trader. As a result, PFOF can manipulate trades at the expense of traders.
This is one of the top reasons why many regulators are working to change the model. Some of the top ECN brokers are FxPro, IG, and EasyMarkets.
Related » What is High Frequency Trading
Examples of leading ECN companies
There are many of these companies in the developed countries. NYSE Arca is one of the oldest players in the industry. Another example is Instinet, a company that is owned by Nomura, a giant Japanese banking group.
Other companies in the industry are Deutsche Bank, BATS, and LiquidNet. BATS is owned by CBOE Global.
Are ECNs market makers?
There is a big difference between ECNs and market makers. As described above (and below), an ECN is a complicated communication system that connects various trading venues and displays prices of key assets like stocks and commodities.
On the other hand, a market-maker is a company that buys thousands of assets and then meets their supply to brokers. They are also known as wholesalers because they hold thousands of stocks, including those that are thinly traded. Market makers make money from the spread of the bid and ask prices.
Citadel Securities has the biggest market share in the market-making industry in the United States. In 2022, the company made over $7 billion in revenue. It is followed by Virtu Financial, a company that is valued at over $3 billion.
Other leading companies in the industry are Jane Street, and Susquehanna among others.
How ECNs work
An Electronic Communication Network is a complex system that is usually designed by some of the biggest financial services companies in the finance industry. They are mostly operated by large companies like Nomura and Deutsche Bank.
These companies design their ECNs and then sell their systems to brokerage companies. The brokerages then display the best prices provided to them by the communication provides.
Prices are usually provided in the form of bids and ask prices. A bid is the highest price that a person is willing to pay for a financial asset while ask is the maximum price that a seller is willing to sell. The difference between the two is known as a spread and what the brokerages take as profit.
The chart below shows how an Electronic Communication Network system works. The ECNs get their prices by looking at all orders that enter the system.
Advantages of ECNs
There are several advantages of using an ECN broker. First, because of their global nature, ECNs have significant liquidity, which means that their execution costs are relatively tiny compared to other companies. As a result, traders often see here smaller fees.
Second, they also operate for a longer period. For example, in the US, brokers are able to offer extended hours trading using ECNs. This is impossible using market-makers because they are usually closed in that period.
Third, many ECN brokers are global entities that are not limited to certain jurisdictions.
Cons of ECNs
ECNs have several disadvantages. The most important disadvantage is that they only execute limit orders when used in extended hours. As such, you cannot open market orders in premarket and after hours.
Another con is that ECN brokers are often not allowed to operate in the US. Finally, you cannot have a direct market access in in these networks.
Summary
In this article, we looked at what ECNs are and how they work. We also looked at some of the top benefits and cons of using these technologies and how they differ with other companies.
Also, we have identified some of the top differences between these communication networks and market makers.
External useful resources
- How do I pick a Electronic Communication Network? – Reddit (r/Daytrading)