As a trader, profitability is the most important thing for you. Without profits, then you are not able to sustain your account for long. So..You want to make sustainable profits for a long period of time.
But don’t fall into a common mistake.Making very huge profits is not sustainable because it puts you in a position of high risk and high reward. As a trader, you need to have the knowledge of various trading strategies; this will help you make money in periods of uncertainties.
One way of achieving this is by combining options strategy in your trading.
Table of Contents
The most known trading strategies
In the past, We have written extensively on day trading strategies. We have explained the various strategies one can use to generate alpha in his day trading.
Some of the strategies We have explained before are:
- Arbitrage
- Hedging
- Scalping
- Events-driven
- Trend following strategies
In this article, as stated above, We will focus on options trading strategies, that is mostly used by major financial institutions and experienced traders.
What is an Option in trading?
Options trading is a form of derivatives trading which gives one a right (but not obligation) to buy or sell a particular asset.
The easiest way to explain this is in form of a farmer who grows soy beans and a buyer. The two wants to maximize their profits. Therefore, if the price of soy beans is $10, the buyer can decide to sell it at the current market price. However, the buyer might approach the farmer and promise him to buy his produce after a month for $15.
The farmer might agree to this because it will assure him a better price in a month’s time. On the other hand, the buyer will benefit in case the price of soy beans rises above $16 during that time.
This is what options is all about. It can be used to speculate the price of currencies, commodities, equities, and other assets.
In options trading, there are mainly three people involved. There is the buyer who is known as the holder and the seller who is known as the writer. For a person to sell you the option, he will need a premium. This is the option’s price.
Options vs Futures
A common challenge among many traders is the difference between options and futures. Unlike options, as we have described above, futures refer to a contract between two or more parties to buy or sell an asset at a later date. Options, on the other hand, give you the right but not obligation to buy or sell an asset at a later date.
There are other differences between the two. For example, in a futures contract, you are required to buy or sell the asset while in options, you could don’t have to buy or sell the asset. Finally, prices in the futures market move quickly, creating more liquidity than in the options market.
The concept of forecasting
To be successful with your options strategy, you need to be good at forecasting. You should be able to tell the direction a certain item will trade at in a given period of time.
As a day trader, you should be able to tell how the price of your instruments will be.
For instance, as an oil trader, you need to have a good idea of how the oil will move within a given period of time. A good example is what happened when OPEC agreed to an oil freeze which was also supported by Russia, and Oil prices went up.
As a wise oil trader, you should have forecasted that the upward trend won’t last a long time because of how OPEC and other oil producers work.
You also need to be good at technical analysis. Technical analysis enables you to use various technical indicators to predict future movements. By combining both technical, fundamental, and sentimental analysis, you will be at a good position to predict how the price will move.
You also need to understand that there is no perfect way of predicting. This will help you reduce your risk exposure.
» Related: What are the benefits of correlation?
The best options trading strategies
#1 – Buy Call
In options trading, one choice you have is known as the Buy Call. Buy call gives you the right to BUY an asset at a specific date and strike price in the future. It however does not give you the obligation to buy the asset or currency.
To do this, the holder will have to pay a premium upfront to the seller of the option. The profit scenario will happen if the asset moves up in price. A good example of this is explained below.
Assume that you are a holder and you buy the option to buy the Euro against the dollar in three months’ time at the strike price of 1.3900. Assume the premium price is $10. If the price of EURUSD is below 1.3910 at expiry, the holder of the pair will not have the incentive to exercise the option. If the price rises on expiry, then the holder will be in a profit position. In this example, if the option expires at 1.3940, then you will make $30.
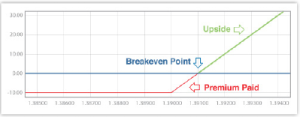
#2 – Sell Call
This is the opposite of the buy call option explained above. In this option strategy, the seller becomes the writer of a call option. Therefore, he will be required to honour the terms of the options contract. A good example is explained below.
if the price rises above 1.3920, the seller will be in the loss area. As a seller, your profit is limited to the premium received but the loss is unlimited.
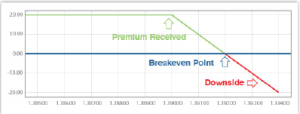
#3 – Buy Put
When you buy a put, you pay a premium to buy the right to sell. The holder of the put option will have an unlimited upside when the spot price moves below the breakeven point.
#4 – Sell Put
As the opposite of buying put strategy, this is an option where the seller becomes the writer of the put option. The seller will receive the option upfront.
Other terms that you must understand when trading options are: expiration date (this is the date when the option contract expires), strike price (price when the option will be exercised), intrinsic value (the difference between predefined rate and the current rate), and money value (difference between the option premium and the intrinsic value of the premium).
Bullish Options Trading Strategies
Long Call
A long call gives traders the right to purchase shares of a stock at a specific price. These options trading strategies offers investors all of the benefits of owning a stock outright while putting much less capital at risk.
Each individual contract controls 100 shares of a stock. If the stock price rises, the upside is virtually unlimited. If it drops, losses are limited to the initial investment.
Coveder Call
In a covered call, investors sell a call option against a stock they hold in an attempt to generate extra income on the asset. These options trading strategies comes into play when an investor likes a stock but has a neutral opinion on its short-term prospects. An investor profits from this strategy when the stock trades relatively flat through the option’s expiration date.
Protective put
A protective put acts as a form of an insurance policy on a stock. The cost of a protective put can limit an investor’s gain if the stock price increases while greatly reducing risk in the event the price of the shares plummets.
Investors often use this options trading strategy in volatile stock sectors such as biotechnology. Important term in options trading for dummies.
Bull call spread
With a bull call spread, an investor buys call options at a certain strike price and simultaneously sells the same number of calls at a higher strike. Investors who foresee a moderate increase in the price of the underlying stock can benefit from bull call spreads.
This strategy offers a slightly limited upside but less exposure to potential losses.
» Related: Risk Management Strategies that work
Bull put spread
In a bull put spread, an investor buys a put option while selling a separate one with a higher strike price at the same time. The investor’s goal is to collect the premium when the shares remain above the higher strike price and the short option expires worthless.
Traders user this a lot as one of their favorite strategy to trade options.
» Related: Spread Trading on the markets
Call back spread
A call back spread is one of the most powerful options trading strategies for volatile stocks expected to undergo major moves. It entails selling a call while purchasing more calls at a higher strike price. If the stock falls, the result is basically neutral. If the stock surges, the upside is virtually unlimited.
Naked Put
With a naked put, investors obligate themselves to purchase a stock at a specific price. The underlying market price is irrelevant. This strategy allows investors to purchase shares of a desirable stock at a discount if the price falls. Investors also collect a premium on the put. Maybe this is one of the most popular options trading strategies.
Pros of trading options
When done right, the options market can be incredibly profitable to traders. It can also help you to hedge some of the risks. Let us look at some of the pros of trading options:
- Hedging risks – You could use options strategy in a bid to lower your risks. For example, if you are long a stock, you could buy a put option of the same asset. As such, if the long trade goes south, you will benefit from the option trade.
- Low-cost strategy – Many online brokers like Schwab and TD Ameritrade have recently lowered their cost of options trading.
- Leverage – It is possible to use leverage to amplify your profits when you are trading options.
- Predict the future – By looking at unusual options activity, you can predict the direction of an asset.
Still, there are some key challenges when trading options such as the relatively difficult path of learning about the industry. In our experience, it is relatively easy to learn to trade normal assets than options.
Also, there is the challenge of liquidity since the sector tends to be relatively illiquid. There are also margin requirements when you are trading options.
External Useful Resources
- Essential Options Trading Guide – Investopedia