Quantitative Easing (QE) is one of the most popular tools used by central banks to handle financial and economic crises. While a form of QE has been used for decades, the current version started in 2009 during the Global Financial Crisis (GFC).
In summary, QE is a process where the Federal Reserve pumps money to an economy in a bid to promote or boost growth and stimulate some inflation. This article will explain the role of the Federal Reserve and how it uses QE to solve major crises.
Table of Contents
Role of central banks in QE
To understand QE, you need to first know more about central banks and their role. A central bank is an independent institution that is given the mandate to supervise the financial sector and set the monetary policy.
In most countries, central banks have what is known as a dual mandate. This refers to the mandate of ensuring that prices are stable and that the economy has a low rate of unemployment.
In most developed countries, the level of price stability is when the rate of inflation is at or below 2%.
Related » Why Jobs Numbers Matters
Other tools
Central banks have many tools that helps them achieve this mandate. For example, they are the only institutions that can set interest rates, which then influences the cost of lending.
When an economy is going through challenges, a central bank can easily slash interest rates. This will in turn incentivize more borrowing and spending. In turn, it will help improve the economy.
During the pandemic, central banks came up with other tools like yield curve control and bond purchases. In yield curve control, a bank comes up with a yield it wants the government bond to have and then buys as much bonds as possible.
Related » What is the yield curve in Trading?
What is quantitative easing?
Quantitative easing refers to a situation where a central bank decides to buy a lot of government bonds to respond to a crisis. It does this by creating money from thin air. This makes the process only relevant to developed countries with a strong currency.
Indeed, the only central banks doing QE are in developed countries like:
- The United States
- Japan
- Australia
- United Kingdom
- The European Union.
These countries have currencies that are widely accepted worldwide. Also, in the past decade, they have gone through a period of low inflation. Therefore, the central banks can afford to print money without risking overinflation.
Related » What you need to know about monetary policy
Developing and emerging markets
On the other hand, many countries in developing and emerging markets cannot afford to use QE. That’s because their currencies are mostly local and have no value outside their borders. As a result, when they print a vast amount of cash, they will create hyperinflation.
How quantitative easing works
The idea behind QE is relatively simple. In times of a crisis, the bond market could become dysfunctional. That’s because many investors will rush to sell the government bonds that they own.
Since bond prices are inverse to the yield, the overall yield will rise and make it expensive for a government to borrow.
QE starts by a situation where the Fed creates new money and then pumps it to the market by buying government bonds. The implication to this is that government borrowing costs plunge.
When interest rates are low and the Fed is pumping money to the market, the impact is that it leads to more government spending. This spending then flows to the market and then stimulates the economy
In extreme cases, the Fed can also pump this debt to other assets other than government bonds. During the Covid-19 pandemic, the Fed bought assets like Mortgage Backed Securities (MBS) and corporate bonds.
This is where the central bank steps in.
Is quantitative easing printing money?
Because of its ability to print money, the bank will decide to do exactly that. It will print money and buy as much government bonds as possible. This will, in turn, make it cheap for the government to borrow money and help to support the economy.
QE during coronavirus pandemic
During the coronavirus pandemic, the Federal Reserve came up with an open-ended quantitative easing (QE) program. In it, the bank set to buy at least $120 billion worth of government bond and mortgage-backed securities as possible.
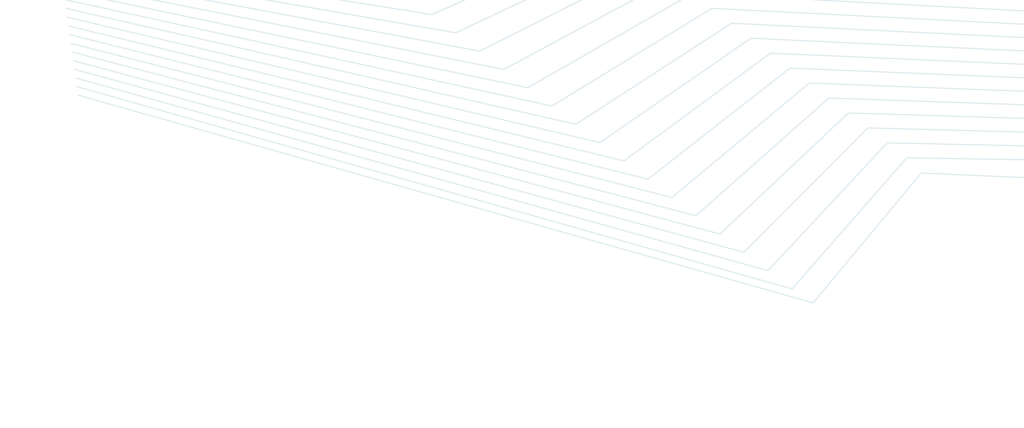
In turn, this led to a substantial expansion of its balance sheet, as shown below.
FED balance sheetIn the European Union, the European Central Bank (ECB) also launched its biggest asset purchase program on record. In total, the bank decided to buy assets worth more than 1.8 trillion euros. Similarly, in the United Kingdom, the Bank of England (BOE) launched a large QE.
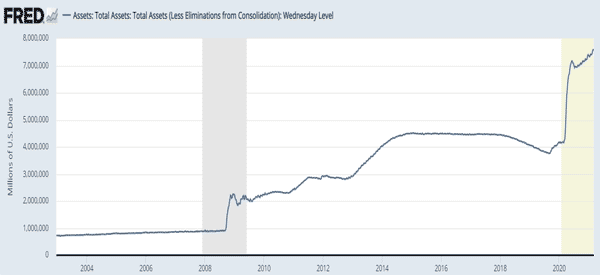
In Japan, the BOJ bought more than $1 trillion in debt. Indeed, the BOJ now holds more than $7 trillion worth of assets. This is substantially higher than the country’s GDP of more than $5 trillion.
Different types of bonds
It is worth noting that the central bank does not limit itself to government bonds in QE. It can also buy other bonds like corporate and municipal. That’s because in times of crisis, investors also tend ti run away from these bonds, leading to inefficiencies. It also buys mortgage-backed securities.
How QE affects the stock market
QE has a major impact on all assets. In most cases, QE leads to robust stock prices because it is usually accompanied by low interest rates. It also leads to excessive funds in the financial market since the Fed is channeling them to financial assets.
There are good examples of this. First, while US stocks dropped sharply during the Global Financial Crisis, they started rising after the Fed slashed rates and started implementing QE. These actions led to one of the longest bull markets in Wall Street.
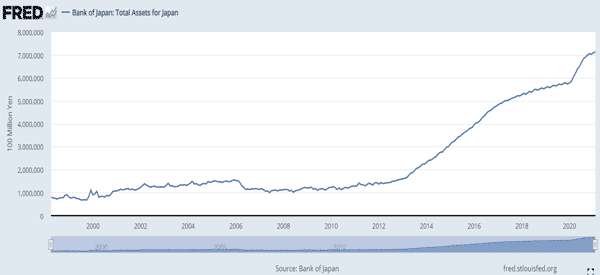
Second, American and global stocks plunged hard as the COVID-19 pandemic started in 2020. They then embarked on another strong rally after the Fed slashed interest rates and started QE.
On the other hand, as shown below, stocks had a difficult time in 2022 as the Fed started implementing quantitative tightening (QT). QT is the opposite of QE and is a process where it reduces its balance sheet.
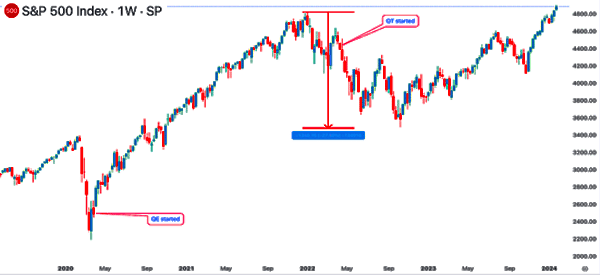
How QE affects currencies
The main issue with QE in the US is that it leads to a risk-on sentiment. It also leads to more dollars being in circulation in the market.
As a result, even when other central banks are implementing their QE, the implication is that the US dollar tends to decline. This happens as traders and investors move to other riskier assets. A good example of this is in the chart below.

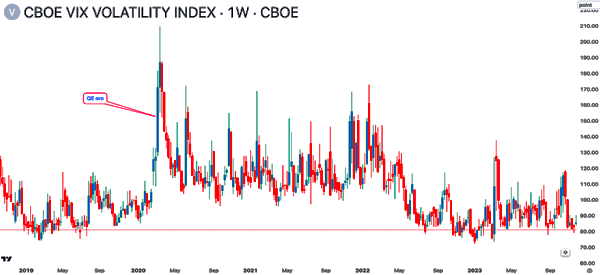
The impact of QE on volatility
QE usually has an impact on volatility in the financial market. In most cases, it usually leads to more inflows as to riskier assets because of low yields in the bond market. In other words, QE leads to animal spirits in the market, which in turn leads to more volatility.
The CBOE VIX index is one of the best tools to measure volatility in the market. It rises when the market is more volatile. As shown below, the index jumped sharply during the QE era of 2020.
QE for traders
Therefore, with all this in mind, how does quantitative easing affect traders? There are several ways this happens.
Complement to lo-interest rates
First, QE is often used to complement low-interest rates. And low-interest rates usually lead to high asset prices because they incentivize more people and investors to buy.
For example, in 2020, when the Fed launched its open-ended QE program, all major assets like stocks, commodities, and cryptocurrencies soared. In other words, QE usually creates a perfect condition for a risk-on sentiment.
Tapering
Second, signs of tapering usually lead to shocks in the financial market. A few years ago, when the Fed started to slow its asset purchases, it led to a situation that is known as taper tantrum. In it, the yields on government bonds rose and stocks fell.
Carry Trades
Finally, QE and low-interest rates usually create a good situation for carry trades. This is where investors borrow in low-interest countries and invest in countries with high-interest rates.
Therefore, this usually leads to a strong performance of emerging market currencies and assets. On the other hand, when QE starts to fade, it leads to weakness in the EM.
Pros and cons of QE
Pros
- Good for risky assets – QE is usually a good thing for risky assets like stocks and cryptocurrencies.
- Stabilize the economy – QE helps to stabilize the economy when it is going through a turmoil.
- Complements interest rate cuts – QE helps to complement interest rates when there is a crisis.
Cons of QE
- Inflated asset prices – In most cases, QE can lead to inflated bubbles in the market.
- Increase Fed balance sheet – It leads to higher assets in the Federal Reserve. For example, QE helped push the Fed balance sheet to almost $10 trillion.
- Inequality – QE is known for promoting inequality because the assets that do well are mostly owned by wealthy people.
Summary
Quantitative easing is an important tool that many developed countries are using to respond to crises. In this report, we have looked at what it is and its implications in the financial market.
External Useful Resources
- What does US bond ‘taper tantrum’ mean for China’s financial markets? – SCMP.com