Companies are always in need for capital, especially during this coronavirus period. To achieve this, firms have several options.
Private companies can sell their shares to the public through an Initial Public Offering (IPO). They can also issue debt by going to banks or issue bonds by going direct to the market. The same is true for public companies.
In this article, we will look at share offerings, what they are, and how to use them in the financial market.
Table of Contents
What is a share offering?
We will start this report with two (quite) recent events.In 2020 Hertz, the global car rental company, filed for bankruptcy. This means that the firm was unable to pay the massive debt it owed. As a result, the company’s share collapsed to almost zero.
But a few days later, the company’s share price started to climb, bringing the bankrupt company’s valuation to more than $600 million. As a result, the company went to the market to raise money through a share offering.
Another example is Ocado, the giant e-commerce company in the United Kingdom.
The company’s share price has been the best-performing in the FTSE 100 as more people embrace online shopping. In May 2020, the company went to the market and raised more than $1 billion by having a share offering. It raised part of the funds by issuing a convertible bond.
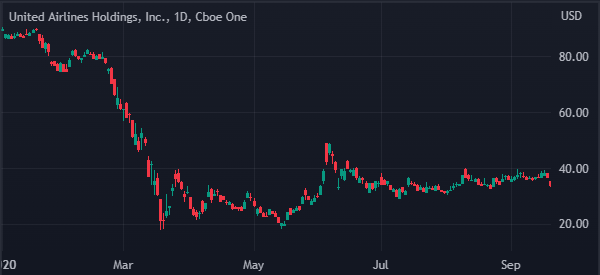
Other companies that have had share offerings in the recent past are United Airlines and DraftKings. The chart shows how the company’s share price declined after it announced its offering.
So, what is a share offering? It is a simple process in which a company issues new shares to investors.
Companies use these funds for a variety of reasons, including:
- handling payroll
- funding an acquisition
- investing in new plants or equipment
- to expand locally or abroad
Share offering vs IPO
A share offering is relatively different than an initial public offering (IPO). An IPO refers to the process in which a private company sells out shares to public investors. It is one of the several process in which a company goes public. The other method that is becoming popular is direct listing, which has been embraced by companies like Warby Parker and Asana.
The IPO process is often long and expensive. First, a company looks for IPO advisors, who include companies like Goldman Sachs and Morgan Stanley. Second, it works with these advisors to come up with the IPO documents like the S1 prospectus. These documents are then filed at the SEC.
Third, the company uses these advisors to do what is known as roadshow. In a roadshow, the company visits some of the biggest investment companies and pitches their investments.
Finally, the company goes public by listing in one of the leading exchanges like the New York Stock Exchange (NYSE) and Nasdaq.
A share offering, on the other hand, is the process where private and public companies raise money by offering their shares. For example, if you are a private company in need of cash, you could sell a stake of the company to a group or a single investor. By so doing, depending on how you structure the deal, it will lead to dilution.
In a public company, a company can have a share offering by just selling more shares in the company. It acts as the opposite of a share buyback. In a buyback, the company uses its cash to buy more stock, which improves its earnings per share.
Another method is reverse merging. We talked about it here.
How secondary share offerings work
The process of launching and executing a share offering is relatively easy. It starts with a public company that has a need for financial resources.
In most cases, the company’s shares need to be performing well for it to attract more bids by investors. The firm needs to get authorization by regulators and shareholders. In the United States, this means talking to the Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC).
After getting authorization from shareholders and authorities, it needs to come up with an offering, mostly at the discount from the current price. Let us look at an example of a share offering.
Example of a share offering transaction
Assume that a company with 1,000,0000 outstanding shares is in need of cash. Also, assume that the firm’s share price is at $50. This means that the company has a total market valuation of $50 million.
Also, assume that the company has a net income of $20 million, it means that the earnings per share is $20 (net income/outstanding shares).
Therefore, the company can decide to have a share offering by giving away 200,000 new shares at $50, which means that it will raise $10 million. These funds will appear in its balance sheet.
However, if the company generates the same net income of $20 million, it means that the earnings per share will be lower ($16.6).
As a result, most shareholders tend to oppose share offerings because they dilute their earnings.
How to trade share offerings
There are two main things to always remember when trading share offerings. First, you need to have access to the latest news of a company. We recommend that you subscribe to various high quality news sources that deliver fast information. You will need this information if you want such offerings.
Second, because of the dilutive nature of offerings that we have mentioned, the stock price tends to drop. However, in most cases, the share price tends to recover if the share offering is justified.
Are share offerings good?
In most cases, existing shareholders do not love it when their companies have share offerings. Besides, it always leads to dilution. However, at times, it is usually one of the best methods of raising capital.
For example, in periods of high interest rates, doing a share offering will save a company money in the long-term.
Also, a share offering can give a company the funds it needs to grow its business. For example, an airline company can raise funds from shareholders with the goal of buying more slots at airports. While such a move will be bad for shareholders initially, the end result will be positive for the firm.
Summary
If you are a trader specialising in stocks, it is important for you to understand how share offerings work and what they mean for stocks.
In this report, we have looked at what these offerings are, their examples. A good way to learn how prices move is to collect companies that have issued additional shares and look how their prices traded afterwards.