A recession is one of the most feared events in the economy. In economics, a recession is defined as a period when an economy contracts in two straight quarters. For example, if an economy contracts by 0.4% in Q1 and 0.2% in Q2, it means that it is in a technical recession.
In most cases, recessions are often associated with major economic crashes such as what happened during the 2008/9 Global Financial Crisis (GFC).
The extreme of a recession is known as a depression. While recessions are common, depressions are extremely rare. The most recent depression happened in 1929.
Another popular word in the market is a stagflation. Stagflation refers to a situation where the slow economic growth coincides with high inflation.
All this are important things for investors because it would wipe out their gains. For traders like you however, there would be no major implications because your goal is to bet on the direction of the market
In this article, we will look at the main causes of recessions and how to trade and invest when it happens.
Table of Contents
Some of the best-known recessions
A common misconception among many market watchers is that recessions happen as a result of the general economic growth.
They opine that asset prices like stocks, bonds, and real estate rises when the economy is expanding and decline when the economy is weakening. This thinking is usually flawed, if you consider what has caused the previous recessions.
Asian currency crisis
In the 1990s, the Federal Reserve left interest rates so low to deal with the Asian currency crisis. This was a period in which a crisis in the East and Southeast. The crisis started in Thailand, with the collapse of the Thai Baht as a result of lack of a foreign currency.
As this happened, other Asian currencies like those of Japan, Indonesia, and South Korea were the most affected. They were followed by Hong Kong, Philippines, and Malaysia.
To prevent the contagion, the Federal Reserve lowered interest rates. As this happened, investors appetite for risk increased in the US and most of them started to invest in risky assets like new technology companies. Ultimately, this ended in early 2000 when the dot com bubble burst.
Dot.com bubble
The dot com bubble led to a global recession as asset prices declined. After the dot com bubble, the Federal Reserve lowered interest rates sharply.
The bank always does this with the goal of attracting more capital to the financial market. As a result of the lose monetary policy, banks started selling credit in large scale. This happened because of the new products, which included the credit default swaps, CDOs, and MBs.
As the Fed started raising interest rates, the delinquencies in the housing sector started piling up. Ultimately, the bubble burst in 2008.
Covid-19 pandemic
Another recession is what happened in 2020 when the Covid-19 illness was declared a pandemic. In its aftermath, the American economy contracted in the first and second quarters, leading to the first recession in a decade.
The recession was short-lived as the Federal Reserve responded forcefully by lowering interest rates and implementing an aggressive quantitative tightening policy.
You can learn more about recessions in CNBC and History Channel.
What causes recessions? A common Misconception
Yield Curve
The most common predictor of when a recession will happen is the yield curve. This is the difference between the longer-term treasury bonds and the short-term ones. In a normal market, the yields of the short-term bonds are usually lower than those of the longer term.
This is because of the premium investors ask for when investing in longer-term bonds. Therefore, this curve usually moves up.
When the yield curve begins to move downwards, investors start to have fear about higher interest rates. In case the yield curve inverts, it will mean that chances of a recession will be higher.
Interest Rates
Interest rates are some of the biggest causes of recessions. Typically, central banks hike interest rates to put brakes on a robust economy. They also hike rates with the goal of fighting inflation. For example, the Fed hiked rates by 450 basis points in 2022 as inflation surged to the highest level in four decades.
Higher interest rates make the prices of sensitive items like cars and houses more expensive. As a result, reduced consumer spending tends to drag the economy into a recession. This is important since consumer spending is the most important part of the American economy.
For example, interest rates had a role to play in the 2008/9 recession. At the time, the Fed was hiking interest rates, which made it expensive for subprime mortgage holders unable to pay their debt.
Natural events
At times, natural events can lead to a recession. A good example is the earthquake that happened in Japan in 2011. In its aftermath, Japan sunk into a minor recession.
Another good example was the Covid-19 pandemic, which led to major lockdowns in most countries. With minor business activity happening, many countries moved into a recession during the year.
Other natural events that can cause a recession are droughts and weather-related ones like hurricanes.
Geopolitics
Further, geopolitical events can lead to a recession. A good example of this was Russia’s invasion of Ukraine in 2022. In its aftermath, European countries that depend on Russia for energy sunk into a recession.
Mergers and Acquisitions
Mergers and Acquisitions (M&A) are indirect indicators of recession. In M&A, large companies usually acquire the smaller ones.
In recent years, the number and size of deals have increased. For example, Dow and Dupont have merged, Microsoft has acquired LinkedIn, Amazon has acquired Wholefoods, and IBM has announced that it will acquire Red Hat.
The size of deals is in these years at all time highs. They have been fueled by low interest rates and the tax cuts. When they happen in large numbers, they can point to more pain in the market as the deals starts to disappoint.
Economic Data
In months before a recession happens, the economic data tends to start disappointing. In recent months, data from the developed countries have been disappointing. This is more important in the US where the housing market has started cooling down.
Similarly, inflation, jobs, consumer confidence, and manufacturing data has been cooling down. The same is true in Europe, China, Japan, and other developed countries. At the same time, the emerging markets are not at ease as higher interest rates raise their borrowing costs.
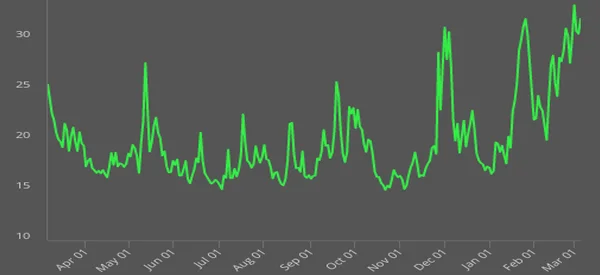
VIX
Another point to consider is the CBOE index (or VIX). The VIX was created to measure the amount of fear that traders have in the market by observing the pricing of the options market.
Even without the VIX, the volatility is evident with the large swings happening in the market.
How to stay protected
While no one can predict accurately when a recession will happen, these numbers are important and should be taken seriously.
As a trader, you will not be affected a lot by a financial crisis. This is because you make money by making short-term trades in diverse assets like stocks and currencies. You are not an investor, who stays invested at all times.
Still, to protect yourself from the adverse effects of a global meltdown, you need to practice safe trading, which means being less over-leveraged and always having a stop loss on all your trades.
As a trader, you should do also the following:
- You should avoid overnight trades.
- The need of size your trades appropriately.
- You should have a stop loss for all your trades.
There are other ways to stay protected during a recession. For example, you should always have an emergency fund that you will use in case market conditions. You can put these funds in a bank account or buy safe assets like money market funds and bonds. Further, you can decide to diversify your financial holdings.
Now that you know what causes recessions and how to protect your money, learn how you can make money with your Trading Office even during a recession.
External useful resources
- Worried about a recession? Don’t panic – CNBC