Mergers and acquisitions (M&A) happen when companies decide to combine in a bid to achieve scale. It has been used by most companies, including Microsoft, Apple, Delta Air Lines, and IBM.
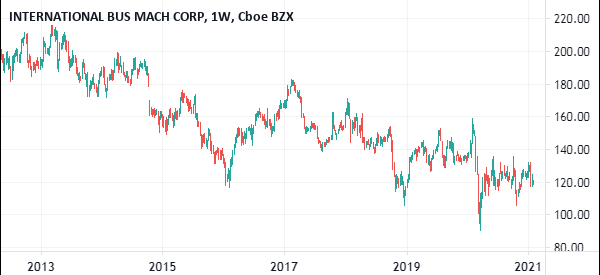
M&A deals soared during the pandemic as interest rates remained low. The volume then declined in 2022 as the Fed hiked interest rates by more than 400 basis points.
This article will explain the concept of Mergers and Acquisitions and what it means for traders.
Table of Contents
What is merger and acquisition?
A merger refers to a situation where two companies join forces. They do this for a number of reasons.
For example, an insurance company in the East Coast can merge with another one in the West Coast. By so doing, the companies will have be at a position to reach more customers.
An acquisition on the other hand is a situation where a larger company acquires another one outright. The M&A industry is a very large one. This year alone, deals worth more than $3.3t trillion have been made globally.
Types of setups under M&A
Other than the typical merger or acquisition, there are several dealings that a company can engage in under the broader M&A structure. This includes:
Asset acquisition
Under this arrangement, one firm gains ownership of another’s assets. It is crucial to note that for such a transaction to take place, a company requires its stakeholders’ consent before handing over its possessions.
Such deals are common when a company is facing bankruptcy. The affected firm can sell its assets to the highest bidder in order to settle its debts.
Consolidation
A consolidation occurs when two companies form a new entity by combining their core businesses and deserting their individual structures. Just like in asset acquisition, shareholders have to approve the proposed setup.
Besides, the investors acquire shares in the newly formed entity. A good example of a consolidation is the one between Bell Atlantic and GTE to form Verizon.
Tender offer
A tender offer is when a company contacts a particular firm’s stakeholders directly with the proposal to purchase the entity’s stock. The offer is usually on a set price as opposed to the market price. In most cases, a tender offer culminates in a merger.
Management acquisition
This arrangement can also be referred to as management-led buyout (MBO). As a way of transforming a firm into a private entity, executives in another company can buy a controlling stake. For instance, Michael Dell, the CEO of Dell Corporation used this approach in 2013 to acquire the company.
Joint ventures
Another way that M&A deals happen is through joint ventures, also known as JV. A JV is a situation where two companies create a partnership deal but retain their corporate identities.
In most cases, these JVs happen for specific projects. Some of the biggest joint ventures in the world are Molson Coors and SABMiller and Microsoft and General Electric.
Why companies do M&A
Companies conduct M&A for various reasons.
Acquiring a Competitor
First, they buy companies with the goal of acquiring a competitor. A good example of this is what Google and Facebook have done.
Google acquired YouTube for about a billion dollars. Today, YouTube is worth more than $200 billion. Similarly, Facebook acquired Instagram for about a billion dollars, and it is now worth more than $520 billion in market cap.
Create synergies
Second, companies do M&A to create synergies. For example, if a software development company has 5000 employees and another software company has 4000 employees, merging the two into one can lead to synergies.
For example, the combined company can have just 5000 employees who will be doing the same thing (like United Technologies and Raytheon).
Accelerate Growth
Third, companies do M&A to accelerate growth. The Facebook example mentioned above is a good one. Facebook realized that its legacy platform will start seeing reduced growth. To accelerate its growth, it acquired Instagram and Whatsapp.
It also sought to acquire Snapchat before it became a public company.
How M&A deals are priced
Companies making acquisitions use different strategies to value companies during merger and acquisitions (M&A). In most cases, companies use their internal teams to value companies. They then combine this with their investment banks who act as their advisors.
Some of the most common investment banks that advise these companies are Morgan Stanley, Goldman Sachs, and Evercore. There are several ways of finding the real value of a company, including:
- PE multiples – Here, they look at the price-to-earnings ratio of a company. This is where they look at the company’s valuation metrics based on its profits.
- PS multiples – This is a multiple that looks at the company’s stock price in relation to its total sales.
- DCF valuation – This is a calculation that looks at a company’s free cash flow and their present net value.
How to trade M&A News
A good way to explain this is the IBM’s acquisition of Red Hat. At its close after the news, Red Hat was trading at $116. IBM will acquire it at $190 per share.
Therefore, when the market opens, the likely scenario is that IBM’s stock declined sharply while Red Hat increased to near $190. This is because IBM has already agreed to pay $190 for the stock.
IBM, instead, dropped for a number of reasons:
- Investors will flee the stock for dilution purposes. They believe that the money would have been better elsewhere.
- The deal will likely increase IBM’s debts.
- Historically, mergers and acquisitions have not worked out as expected. In fact, they have been value destroyers. A good example of this is the acquisition of Monstanto by Bayer. After the deal was closed, Monsanto lost a major lawsuit that threatens its existence.
Therefore, when a deal is announced, the best way to trade is to go long the company being acquired and shorting the one doing the acquiring. In fact, this has created a large group of investors who specialize in what is known as merger arbitrage.
Where to find M&A news
- SeekingAlpha
- CNBC
- Reuters
- Bizjournals
- MarketWatch
How to deal with M&A rumours
A key feature of M&A is the rumours that happen before deals are announced. In most cases, prominent media companies like the Wall Street Journal (WSJ), Bloomberg, and Financial Times tend to write news about potential deals.
In some cases, companies tend to be accurate and in other periods, these companies tend to deny the rumours.
So, how do you trade these rumours?
One of the most popular approaches is to buy shares of the company being acquired and those doing the acquiring. In other situations, you can use the scalping strategy, where you scalp the company being acquired.
Since these stocks tend to trade in a tight range, you can scalp them by taking advantage of those small movements.
How do stocks perform during a merger/acquisition?
In the event of a merger or acquisition, the share prices of the two companies usually move in opposite directions. This situation is usually on a short-term basis before the operations stabilize.
On the one hand, the shares of the acquiring firm fall. This is because the company may have used a substantial amount of its funds or even entered into debt that the shareholders think was too high.
In contrast, the stock price of the acquired firm is likely to rise. This is after the acquiring corporation pays a substantial amount to entice the shareholders.
External Useful Resources
- List of largest mergers and acquisitions – Wikipedia