Monetary policy refers to most decisions and actions made by a country’s central bank. These actions mostly include policies on interest rates, currency swaps, quantitative easing, and quantitative tightening policies.
Monetary policy is often confused with fiscal policy. Fiscal policy refers to actions that are implemented by governments. These policies include budgets and stimulus policies. In this article, we will focus on monetary policy actions and their impact on the financial market.
Table of Contents
Central Banks: what they are…
The reality is that the central bank and the presidency are very important in an economy. It is also difficult to separate the two about the status of the economy. The president of the country, through his executive leadership is usually responsible for the fiscal policy.
A good example of this was the passed tax reform package that slashed taxes for companies and individuals. In the Obama era, an example of the fiscal policy was on the Dodd Frank regulations which were meant to make the US economy safer to avoid another financial crisis.
On the other hand, central banks like European Central Bank (ECB), Fed, and Reserve Bank of Australia (RBA) are responsible for the monetary policy. The president – or governor – of the central bank is usually nominated by the president and confirmed by the legislators.
Their role is to ensure the safety of the financial markets and protect the consumers.
On the latter, they protect the consumers from increased inflation. They do this using the various tools, with the main one being interest rates.
The central banks are responsible for supplying money to the economy. This money is usually produced and lent to financial institutions at an interest rate.
…and how they works
When the economy is doing terribly, the central banks can lower the interest rates to spur growth. This growth happens as more people borrow money to invest and consume.
This is what happened during the financial crisis of 2008/9. The central banks from around the world brought interest rates to zero and started an experiment known as quantitative easing.
In this program, they printed money and bought financial assets like bonds and treasuries.
On the other hand, when the economy is doing very well, the central bank tends to hike interest rates. They do this to prevent the economy from overheating. The economy overheats when more people are employed and have more money, which leads to overconsumption.
This puts the economy at a tough place, especially when it starts to slow down.
Dovish vs Hawkish meaning
Two common terms when it comes to central bank officials are dovish and hawkish.
Dovish refers to a period when a central bank or officials have shifted their focus to easing monetary policy. For example, when the bank is considering more rate cuts, it is said to be dovish.
A hawkish policy, on the other hand, is a situation where a bank’s officials are considering rate hikes and quantitative tightening.
Related » How to Predict the Chance of a Fed Rate Hike
Practical Example
A good example for this is to assume that you have a lemonade stand. In a normal month, you serve 10 customers. Then, in one month, the number increases to 15 and 20 in the following month. The number keeps on growing. To serve these new customers, you need to take a loan from the bank.
The problem will come when the number of customers start to slow to the normal number. If that happens and you have a loan, you could be in trouble paying the loan.
As a trader, everything that happens to the markets usually leads to the Fed. When the inflation rate is growing fast, it usually leads to tightening. You should always read the minutes of the Fed and listen to the minutes from their minutes.
How central banks affect forex prices
The decisions made by a central bank are influential to the relevant currency, as well as other currency pairs. This is founded on the fact that several currencies can be tied to one currency.
For instance, the Hong Kong dollar is pegged to the US dollar. As such, policy changes by the Federal Reserve are bound to affect the value of the Hong Kong dollar. A similar setup is observable with the Belgian Franc, which is pegged to the Euro.
Related » Understanding Currency Pairs Correlation
A central bank affects forex prices through its press releases, speeches, and policy changes. Investors often focus on the tone of the speech, as well as its content.
Impact in the US dollar
For instance, the US dollar tends to appreciate in value when the Federal Reserve’s tone is hawkish. This means that the bank supports an increase in interest rates as a way of dealing with inflation.. even if it impacts employment and economic growth.
Conversely, a dovish tone may cause the greenback to decline in value.
How central banks control currency supply & demand
As part of its role, central banks control money circulation. The applied approach depends on the health of the economy. One of the easiest ways is to print money. However, this is not the most effective means as it may result in inflation.
The central bank can also decide to adjust the reserve requirement for financial institutions. This is the minimum amount of funds that a bank should retain in its reserves. To increase the supply of money, a central bank can lower the reserve requirement.
Subsequently, the banks will be able to lend more money to their clients. To lower inflation and lessen the funds in circulation, the central bank can increase the reserve requirement.
Central banks can also use a quantitative easing (QE) program or adjust interest rates. The QE approach helps lower interest rates.
With low interest rates, banks are in a position to lend more money to their customers. Subsequently, there will be a higher supply of the currency in the market.
Related » Understand supply and demand
How Central Bank decisions impact stocks
Central bank decisions have an impact on all assets, including stocks. Stocks are affected by monetary policy in a number of ways.
Fed’s losing monetary policy
First, ideally, stocks tend to rise when the Fed embraces lose monetary policy. A good example of this is what happened after the Covid-19 pandemic broke.
At the time, the rate cuts and quantitative tightening led to a strong performance of the stock market. There are a number of reasons why this happens. First, when rates are low, people tend to move their funds to riskier assets because of the negative yields that happen in the bond market.
Corporate consolidation & access to cash
Second, a period of low-interest rates tend to spur a wave of corporate consolidation, which is usually bullish for the stock market. Finally, companies usually have easy access to cash, which they use to reward their shareholders. Firms also spend less money paying interest payments.
Tightening phase
On the other hand, tightening by the Fed usually leads to weak performance in the market. The chart below shows how American stocks crashed after the Fed started hiking interest rates in 2022. This situation is usually known as not fighting the Fed.
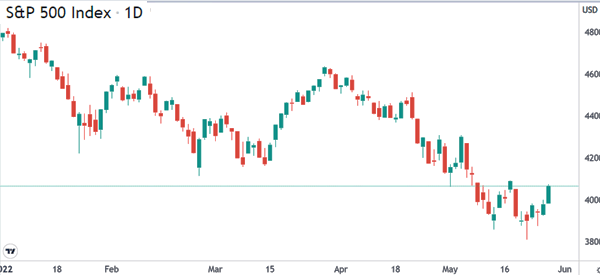
It is worth noting that some market sectors react differently to monetary policy.
In theory, companies in the financial sector like insurance and banks tend to underperform when the Fed is dovish. This happens because they usually generate less interest income when rates are low.
How the Central Bank Works :UsefulTips
- Learn More On – Europa.eu